Parts of the Human Brain
The human brain is the most incredible computer on earth, and brain scientists are only just beginning to understand how our brains work. Let’s look at the main structures of the brain and their important functions.
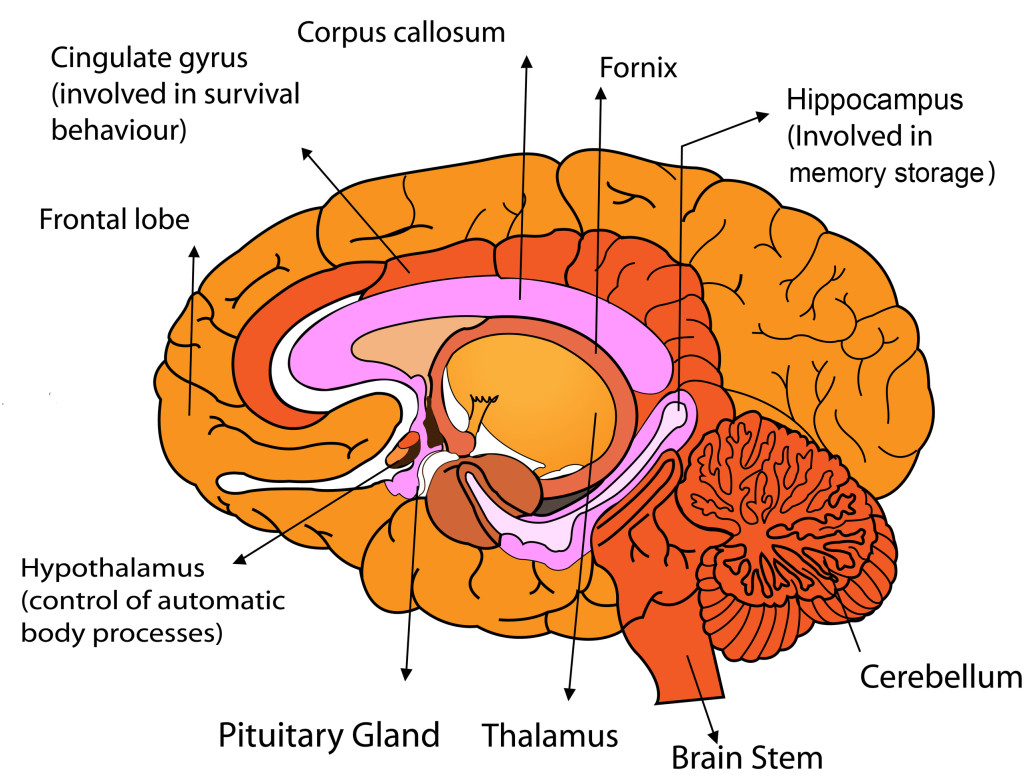
Frontal lobe – This is the front-most section of the cortex (the thick, folded outer part of the brain also known as ‘grey matter’) and is more developed in humans than in any other animals. It is important in reasoning, planning, movement, long-term memory, reflection, emotional expression, and some eye movement.
Corpus callosum – This is a bundle of fibres that connects the two halves, left and right, of the brain together.
Cingulate gyrus – Above the corpus callosum, the cingulate gyrus is not well understood but is linked to memory, forming and processing emotions, and learning.
Thalamus – The thalamus is a round structure found right in the center of the brain. It’s responsible for regulating sleep and waking, as well as sending sense and motor signals to the cerebral cortex for processing.
 Hippocampus – This small brain part was named after the Latin word for seahorse because of its shape. It plays a major role in short and long-term memory as well as spatial memory and processing.
Hippocampus – This small brain part was named after the Latin word for seahorse because of its shape. It plays a major role in short and long-term memory as well as spatial memory and processing.
Hypothalamus – This small structure has a big job. It controls body temperature, blood pressure, sleep and waking cycles, hunger and thirst, and automatic fear behavior.
Fornix – The fornix is an arching structure that curves around the thalamus and carries signals from the hippocampus to the hypothalamus.
Cerebellum – Cerebellum is Latin for “little brain” and this structure at the back of the brain is largely responsible for fine motor control, balance, and learning of movement.
Pituitary gland – The little pituitary gland also has a big job. It releases hormones (chemical signals) that control the body’s rate of growth, aging, and sexual maturation.
Brain stem – at the bottom of the brain, the brain stem connects the brain to the rest of the body and allows the brain to receive information from the senses and send signals to control muscles. It also helps to regulate breathing and heartbeat.