States of Matter
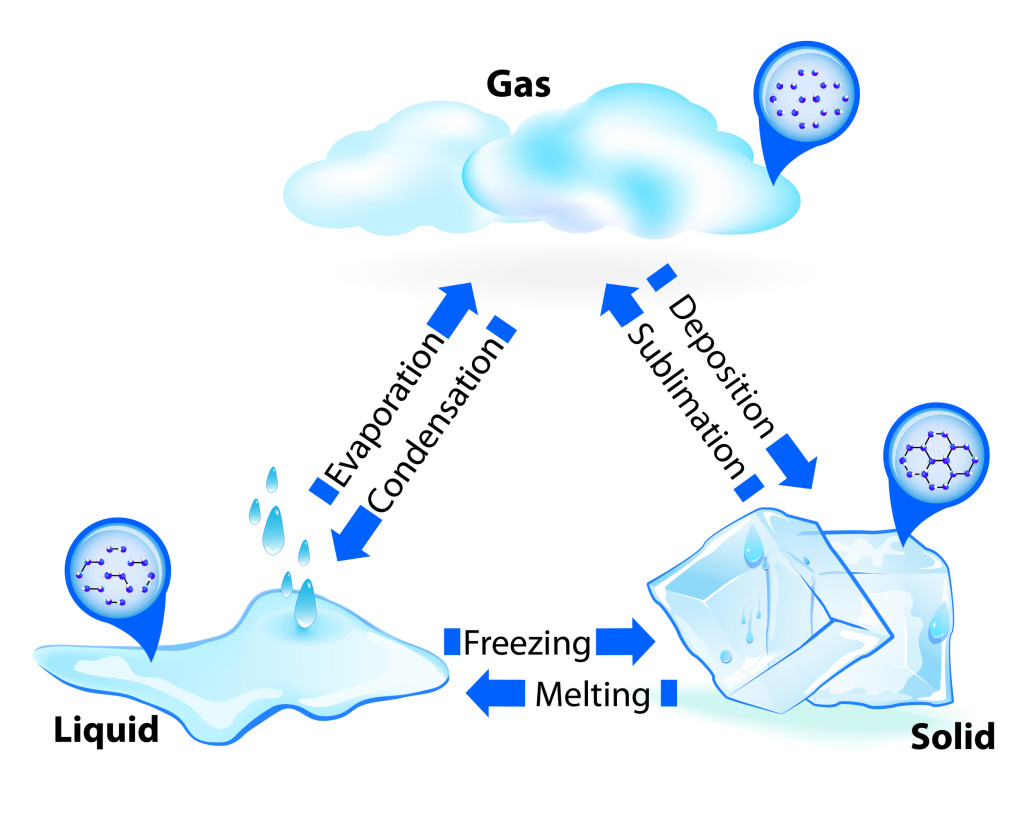
A states of matter is a physical condition that any object or substance can be in. There are many possible states, but the 3 most common ones, and the ones that we see around us on a daily basis, are solid, liquid, and gas.
A substance in solid state is solid! This means that the atoms that make it up are tightly packed together and there are strong bonds between them that require lots of energy to break. Solids have definite shapes and definite volumes. When energy is introduced into a solid in the form of heat, it can melt to form a liquid, such as when ice melts into liquid water. A solid can also turn directly into a gas if enough heat and pressure difference is available, such as ice turning to water vapour under hot sunshine and dry wind. This is called sublimation.
Liquid
A substance in liquid state has more energy than in solid state, and this energy allows for its particles to move around more freely, through there are still some bonds holding atoms and molecules together. This allows liquids to change shape to fill containers, but no to change volume. If a liquid loses enough heat energy, its molecules will start to bond back together and assume a set shape, and this is what we call freezing. However, if the molecules receive a lot more energy, they will be able to spread out and break the bonds between them, turning into a gas through evaporation.
Gas
A substance in gas form has very weak bonds between its molecules, allowing the gas to expand or be compressed, changing both shape and volume. When a gas is cooled, its high-energy molecules slow down and come closer together, and it becomes a liquid through condensation. A gas can also turn directly into a solid without first becoming liquid first, if temperature drops while pressure rises, just like when cool moist air freezes into frost on a window. This is called deposition.
Find out more about winter solstice!