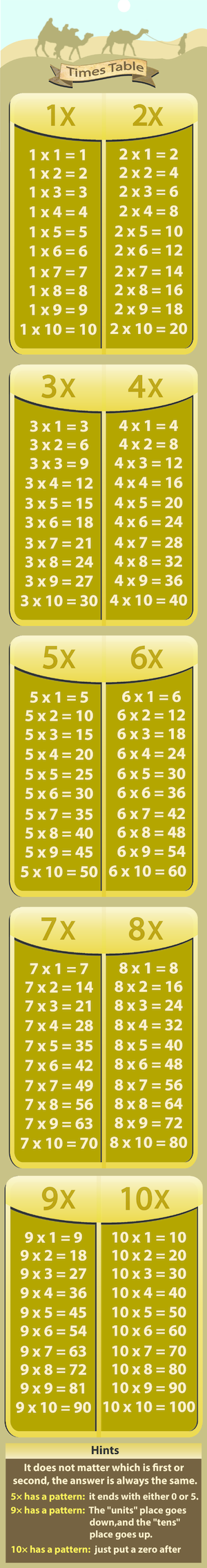Photosynthesis
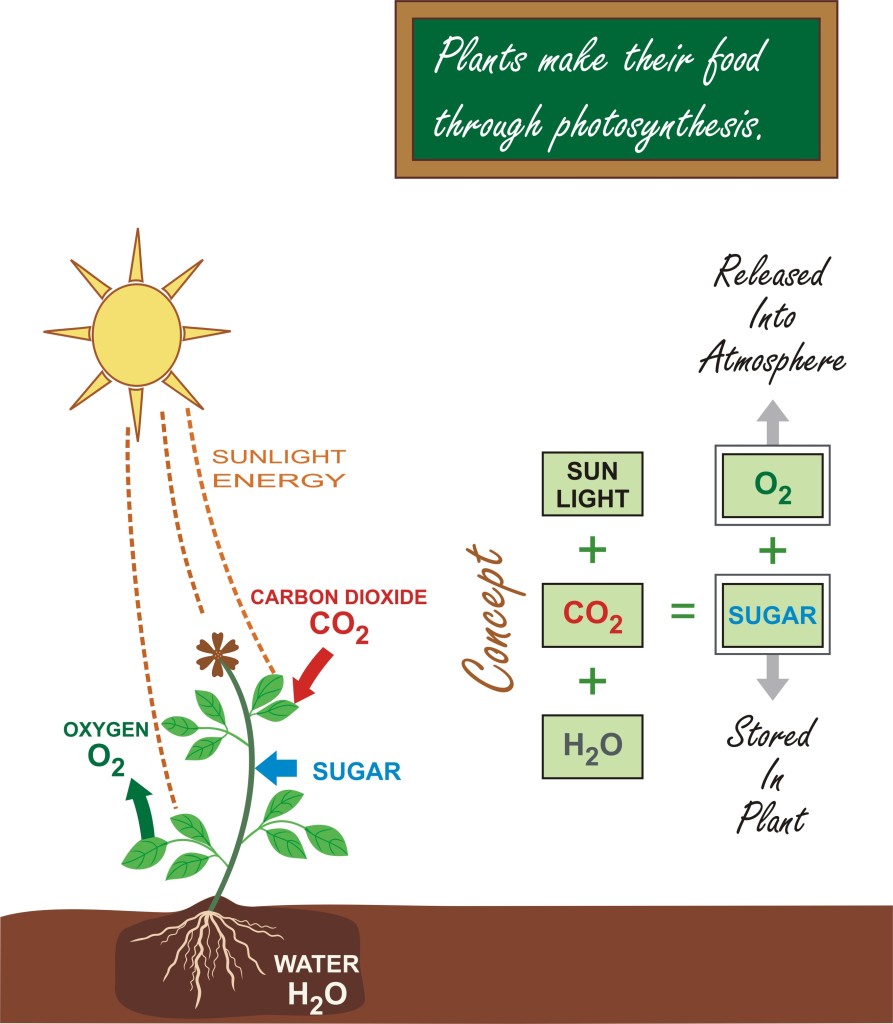
“Photo” means light and “synthesis” means making or putting something together, so like most scientific names, this term tells you at least a bit of what it’s about. Photosynthesis is the name we give to the process that most algae, cyanobacteria, and plants use to make their own food using the power of the sun. Let’s focus on plants to understand how photosynthesis works.
Water + Carbon Dioxide
Plants take in water through their roots and pull it up to their leaves. Small holes in the leaves, called stomata, take in carbon dioxide from the air into the plant. Leaves are also the sites where most photosynthesis in plants takes place, since this is where most of their chloroplasts are located.
Chlorophyll
Chloroplasts contain the chemical chlorophyll, which is in important molecule used to absorb the sun’s energy. Chlorophyll absorbs blue and red wavelengths of light, but it reflects green light, and that’s why we see most plants (and algae) as green!
Sunlight
The energy of the sun is essential for photosynthesis, and that’s why plants build themselves large, branching green leaves to capture as much sunlight as they can. Sun light gives the energy to power the chemical reaction that is photosynthesis.
Chemistry
Sunlight allows plants to break up the molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), and then re-form them into carbohydrates (CH2O) and oxygen gas (O2). These carbohydrates are then used as food for the plant, just as our bodies use the carbohydrates in plants as our own food. As for the oxygen, photosynthesis is responsible for creating nearly all of the oxygen in our atmosphere, which is useful if you like breathing!